IOPS Results
Random Reads (4 KiB)
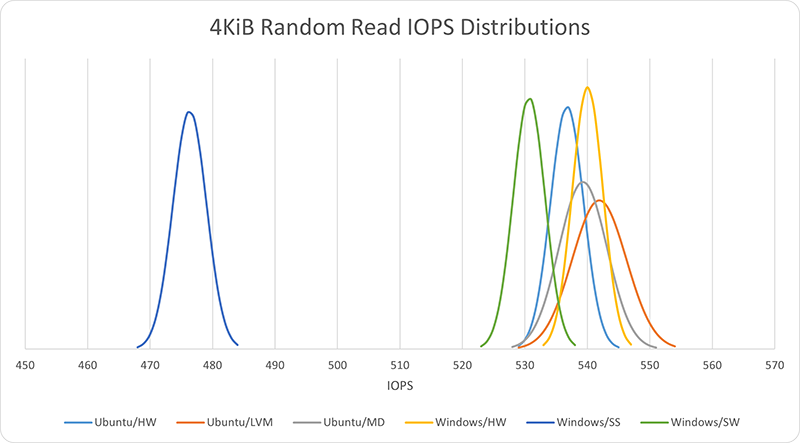
Small random read performance was very good in general across all storage methods. The best performance was from Ubuntu LVM, with all but Windows Storage Spaces coming in close behind. Among the leading cluster, Windows software RAID was noticeably behind the others, but not by much. Windows Storage Spaces was the lone outlier, at only 88% of the performance of the leader.
| I/O Method | IOPS | s |
|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu/HW | 536.8 | 2.65 |
| Ubuntu/LVM | 541.9 | 4.33 |
| Ubuntu/MD | 539.3 | 3.85 |
| Windows/HW | 540.1 | 2.46 |
| Windows/SS | 476.4 | 2.70 |
| Windows/SW | 530.7 | 2.55 |
Random Writes (4 KiB)
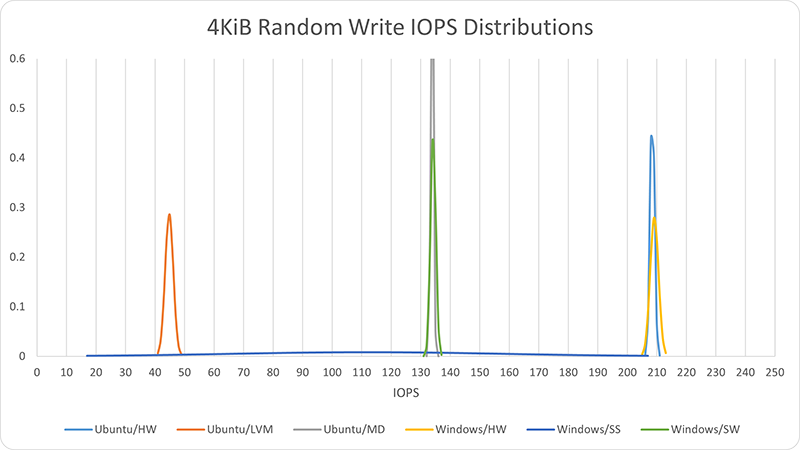
Small random write performance varied widely. Hardware RAID is the obvious leader for this I/O method, with both Linux and Windows showing nearly the same IOPS (208.5 and 209.1, respectively). Ubuntu mdadm and Windows software RAID scored very closely (133.9 and 134.2 IOPS, respectively), with Windows Storage Spaces not far behind (112.1 IOPS). However, Windows Storage Spaces performance showed a huge variance (s=46.1), as shown by the very flat distribution compared with the others. Surprisingly — to me — Ubuntu LVM was by far the worst performer (44.9 IOPS, 21% of the leader).
| I/O Method | IOPS | s |
|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu/HW | 208.5 | 0.76 |
| Ubuntu/LVM | 44.9 | 1.39 |
| Ubuntu/MD | 133.9 | 0.49 |
| Windows/HW | 209.1 | 1.42 |
| Windows/SS | 112.1 | 46.14 |
| Windows/SW | 134.2 | 0.90 |